What Color is Emerald: In-Depth Analysis
Emeralds are well-known and admired for their stunning green color. This captivating hue sets them apart from other gemstones and contributes to their overall allure. The color of an emerald can range from lighter shades of green to darker, more intense tones, but they are always characterized by their signature green shade.
The vibrant green color of an emerald is a result of trace amounts of chromium and/or vanadium replacing aluminum atoms within the crystal structure. This unique feature is essential in distinguishing emeralds from other green gemstones and is interesting to learn about when exploring the world of precious stones.
So, when you think of emeralds, keep in mind that their distinctive color comes from a combination of elements, making them stand out in the gemstone world. Each emerald has its shade of green, but no matter the variation, their beauty is undeniable.
Color Characteristics of Emerald
| Color Grade | Color Description |
|---|---|
| AAA | Exceptional, vivid green with little to no visible inclusions |
| AA | Very good, rich green with slight inclusions visible under close inspection |
| A | Good, medium green with visible inclusions that do not detract from overall appearance |
| B | Fair, light to medium green with noticeable inclusions that may impact appearance |
| C | Poor, pale green with prominent inclusions affecting overall transparency |
Understanding Green Hues
The color emerald is synonymous with an alluring and vibrant shade of green. It belongs to the green gem variety of beryl. When discussing emerald hues, the focus is primarily on color rather than factors like clarity or brilliance. The rich green color found in emeralds can vary slightly in saturation and tone, making each stone unique in its appearance.
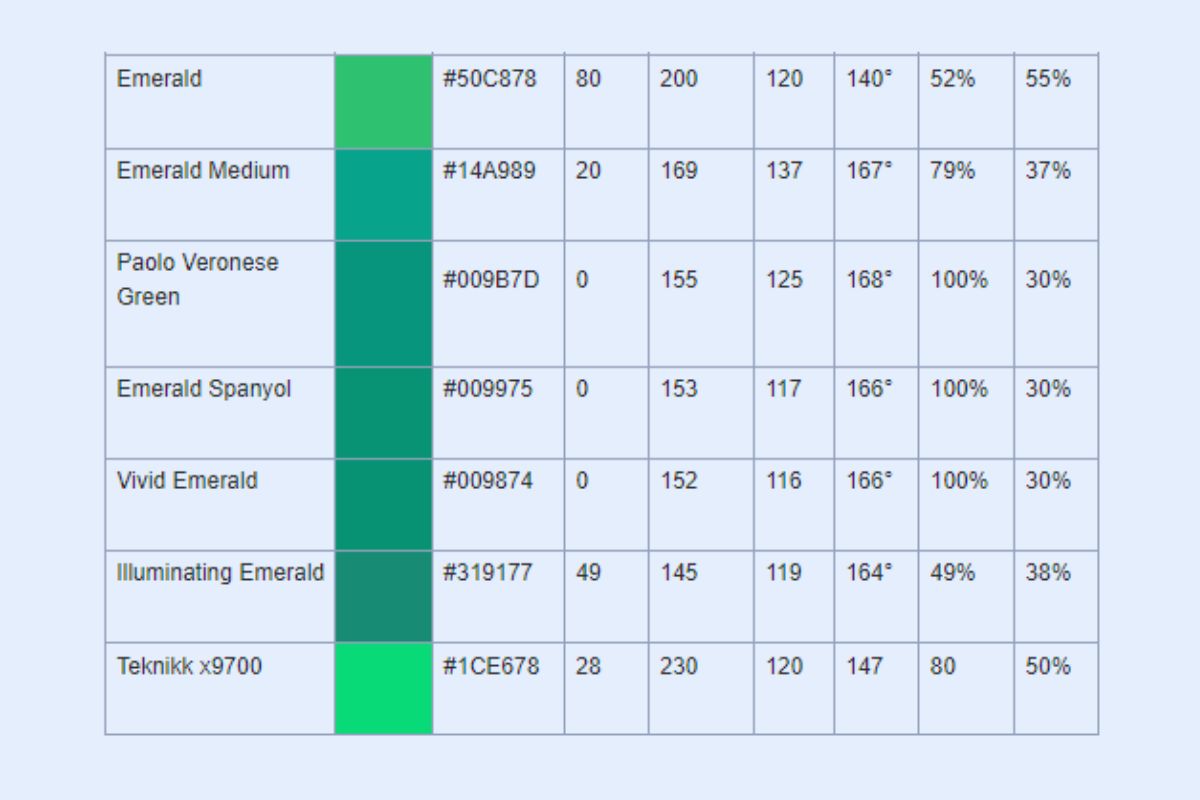
Emerald Hex and RGB Values
To better understand emerald's color, we can examine its hex and RGB values. In the hex color code system, emerald is represented as. This code may help you replicate the vibrant green hue of emerald in digital designs or artwork. In the RGB color model, emerald has the RGB values R: 80, G: 200, and B: 120. These values indicate red, green, and blue components that blend together to create the unique tone.
CMYK and HSV Models
Another way to understand the color characteristics of emerald is through the CMYK and HSV color representation models. In the CMYK model, the color is defined by the percentage combination of cyan, magenta, yellow, and key/black. For emerald, the CMYK values are:
- Cyan: 60%
- Magenta: 0%
- Yellow: 40%
- Key (Black): 22%
In the HSV model, the color is defined by its hue, saturation, and value/brightness. For emerald, the HSV values can be described as:
- Hue: 140°
- Saturation: 60%
- Value: 78%
By understanding these values, you can better grasp the makeup of the notable green hue of emerald in various color systems, helping you in your creative process or decision-making related to this rich shade.
Emerald in the Gemstone Context
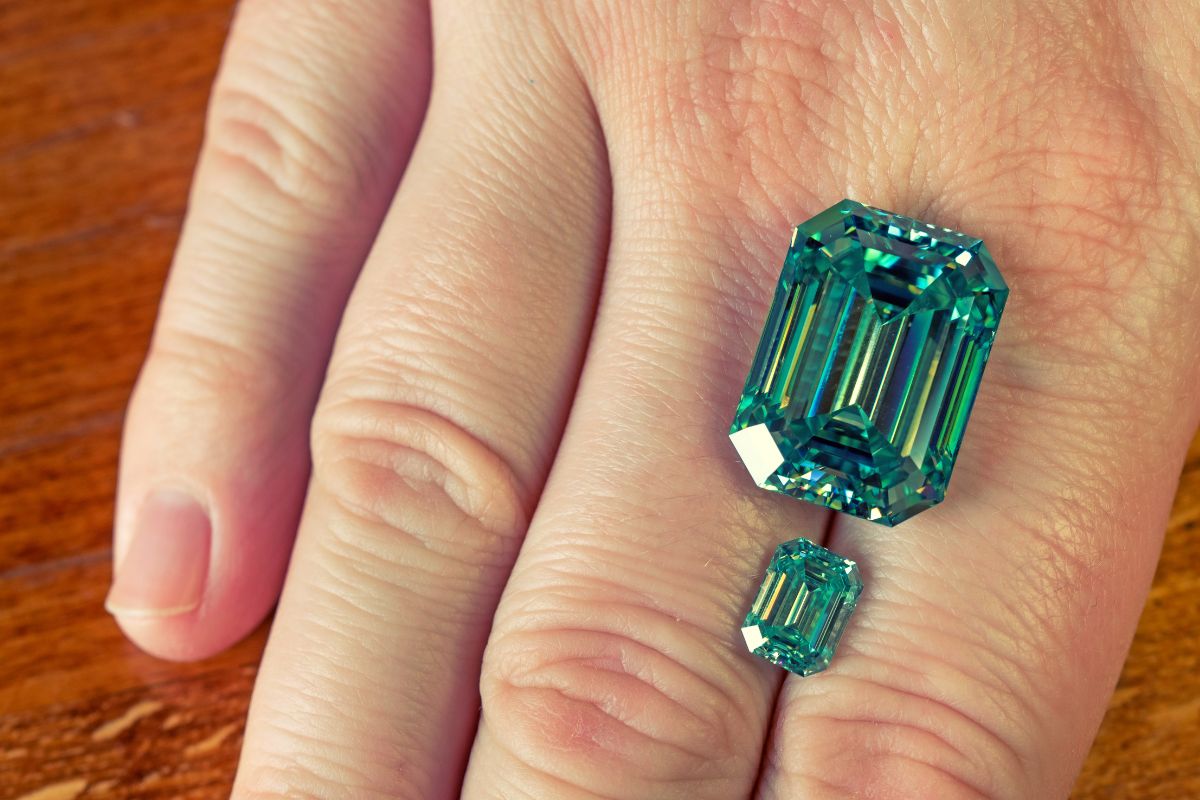

The Significance of Emerald Green
Emerald, a valuable and timeless gemstone, is prized for its distinct and vibrant green color. The captivating emerald green shade evokes a sense of luxury, sophistication, and deep connection to nature, making it highly desired in the world of jewelry and fashion. As you explore the allure of emeralds, you'll discover that their unique hue plays a critical role in their overall value and appeal.
Physical Properties of Beryl
Emeralds belong to the beryl mineral family, a group that also includes other famous gemstones such as aquamarine and morganite. Beryl, in its pure form, is colorless. The emerald green color emerges as a result of trace elements like chromium and vanadium present in the crystal structure. The variation in the amount and type of these elements can cause subtle differences in the green shade of emeralds, from bluish-green to slightly yellowish-green.
Emerald Quality Factors
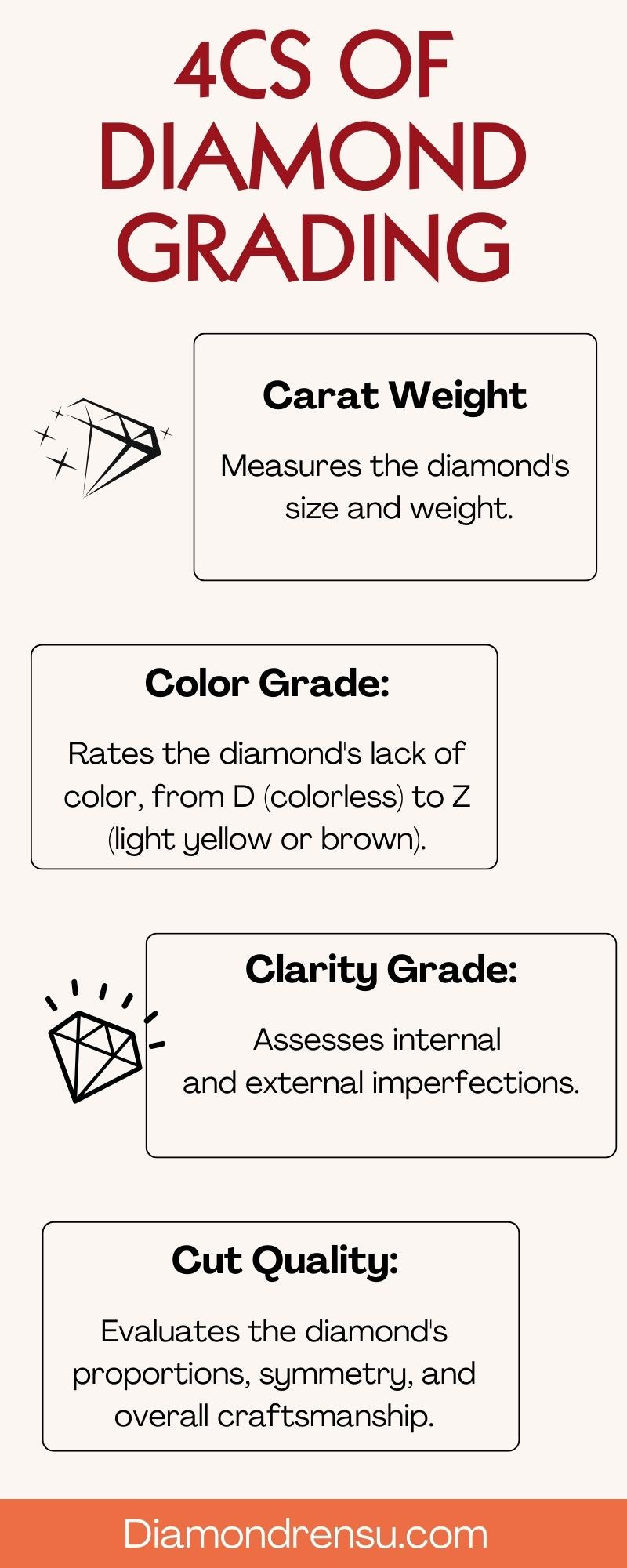
When evaluating an emerald, gemologists consider the 4C's: color, cut, clarity, and carat weight. Each factor contributes to the overall quality and value of the gemstone.
- Color: The most important aspect of an emerald is its color purity and saturation. The most valuable stones display a rich, verdant green hue with even color distribution.
- Clarity: Emeralds are typically faceted to enhance their clarity. Inclusions, also known as "jardin" (garden), are common in natural emeralds, and some might find them charming. However, stones with excessive inclusions affecting transparency or structural integrity are less valuable.
- Cut: Skilled artisans cut and polish emeralds to maximize their color intensity and brilliance. Cuts, such as the signature emerald cut, enhance the gemstone's beauty while minimizing the visibility of inclusions.
- Carat weight: Large, high-quality emeralds are rare, which means their value increases significantly with size. The carat weight plays a crucial role in determining the price of the gemstone.
It's important to note that many emeralds undergo treatments to improve their color and clarity. While treatments are common in the gemstone industry, disclosure and identification of these enhancements are essential for ethical reasons and to maintain the trust between buyers and sellers.
By understanding the gemstone context and quality factors of emeralds, you'll appreciate the beauty and value of these iconic green treasures even more.
Emerald Across Cultures and History

Symbolic References to Emerald
Emerald, a rich green gemstone, has held cultural significance throughout history. In different cultures and time periods, the color emerald has symbolized various concepts. For example, in Ireland, the "Emerald Isle", it represents the lush green landscapes the country is known for. In many societies, the color emerald is associated with the rejuvenating season of spring as it captures the vibrant shades of new growth.
In ancient Egypt, emeralds were highly valued and considered a symbol of fertility and rebirth. The Egyptians crafted beautiful jewelry with emeralds and even used the color in their artwork. In Arabic culture, the emerald has a rich history as the mystical Emerald Tablet, an ancient text believed to contain the secrets of alchemy and the philosopher’s stone, which can supposedly turn lead into gold.
Historical Emerald Mines
Emeralds have been mined all around the world, with some of the most famous mines originating in Colombia. It is believed that the indigenous people of Colombia began mining emeralds as early as 500 CE. Colombia’s Chivor and Muzo mines are some of the most renowned sources of high-quality emeralds. Currently, Zambia is another significant producer of emeralds. The Kagem mine in Zambia is the largest emerald mine in the world.
Legends of the Emerald Tablet
The Emerald Tablet, as mentioned earlier, is a legendary artifact in the history of alchemy and the Hermetic tradition. The text, believed to have been written by the legendary sage Hermes Trismegistus, is said to be engraved on an emerald tablet. The teachings inscribed on this tablet have held significant influence on the development of alchemy, Western mysticism, and even the modern practice of chemistry.
The tablet's translation into various languages over centuries has led to various interpretations and spawned legends about its power and secret wisdom. While the true origins of the Emerald Tablet remain a mystery, the rich history of symbolic references and the allure of this fabled artifact captures the imagination and demonstrates the lasting impact of emeralds across cultures and throughout history.
Variations and Comparisons of Green
Natural Spectrum of Green
In the natural spectrum of green, there is a diverse range of hues that can be observed in various settings. From the lush jungle green of a tropical rainforest to the calming sea green of ocean waters, green colors can evoke an array of emotions and associations. Even within the realm of plants and foliage, you can find shades like moss green, pine green, and forest green. As you explore the world around you, consider the variations of green that you may encounter, and how these different shades may complement or contrast with the vibrant green of emeralds.
Emerald and Pantone
The green color of an emerald is a unique shade, made even more distinct when compared to the Pantone color system. Pantone, a standardized color matching system, categorizes and labels various shades for consistency in design and manufacturing. While the specific shade of an emerald may not be directly represented in Pantone's color palette, it falls within the general range of shades that include olive green, hunter green, and artichoke green. By using Pantone colors as a reference point, you can appreciate the distinctive hue of emeralds in relation to other shades of green.
Comparing Different Shades of Green
To better understand the unique shade of an emerald, let's compare it to a few other shades of green. Here are some notable examples:
- Jungle Green: A deep, rich green often found in lush vegetation.
- Sea Green: A lighter, more muted green with a hint of blue undertones reminiscent of ocean waters.
- Moss Green: A more earthy, subdued shade of green found in the natural world.
- Pine Green: A darker, cooler-toned green similar to the color of pine tree needles.
- Forest Green: A deep, darker green found in dense forests and woodlands.
- Olive Green: A muted, earthy green with hints of brown and yellow tones.
Emeralds exude a brilliant, intense hue that sets them apart from other greens. This striking color, creating a distinctive appeal and beauty, is prized in the world of gemstones. As you continue to explore various shades of green, keep in mind the special characteristics that make emeralds stand out among the rest.
Scientific and Artistic Considerations
Color Science and Perception
In the world of color science, colors are often defined by their position in various color spaces. For instance, the RGB color space combines red, green, and blue primary colors to create a wide range of hues. Emerald, a shade of green, can be represented using hex code as #50C878. This corresponds to an RGB value of (80, 200, 120) with green being dominant. Similarly, the PMS (Pantone Matching System) helps in accurately standardizing colors.
The way you perceive emerald green is influenced by factors such as chroma, lightness, and brightness. These are properties inherent to colors that help you distinguish them from one another. For example, the Munsell color system associates colors with specific numerical values in terms of hue, value, and chroma scales. By understanding these scales, you can appreciate how emerald green varies in relation to other colors like cyan, magenta, yellow, red, and blue.
It's crucial to recognize that color perception is subjective, and individual experiences might differ. Factors like lighting conditions and the presence of other colors nearby can impact the way you perceive the emerald hue.
Emerald in Art and Design
In the realm of art and design, emerald green has long been admired for its rich, lustrous appearance. The emerald color carries a mix of historical significance and contemporary relevance, making it a popular choice in various forms of art. One well-known pigment used for achieving this stunning color is emerald green (Cu(C₂H₃O₂)₂·3Cu(AsO₂)₂), which can be found in many historic paintings. However, be aware that this pigment, as mentioned in this study, may chemically degrade over time, altering its appearance.
When incorporating emerald green in design, consider its impact on visual elements. The harmony between colors can evoke different emotions and influence aesthetics. Designers can use tools like color wheels and color theory principles to create captivating compositions. Using contrasting colors, such as red or blue, can make emerald green stand out, while utilizing analogous colors like cyan or yellow can create a more subtle, harmonious effect.
Overall, it is essential to understand the scientific and artistic aspects of emerald green to fully appreciate its beauty and incorporate it effectively in various projects.
Emerald as a Precious Gemstone

Emerald is a highly prized gemstone known for its captivating green color. As a variety of the mineral beryl, it is also the birthstone for May. Typically, the color of an emerald ranges from light green to a deep, rich green. The green hue is due to trace amounts of chromium and vanadium in its chemical composition. With a refractive index of 1.567 to 1.590, birefringence of 0.005 to 0.009, and a specific gravity of 2.72, emerald has unique optical and physical properties that distinguish it from other gemstones. The most famous sources for emeralds include Colombia, Zambia, Brazil, and Ethiopia.
Evaluating Emerald Quality
When assessing the quality of an emerald, gemologists consider the 4 Cs:
- Color: The most important factor, the ideal emerald should possess a vivid green color.
- Clarity: Emeralds often have inclusions, also known as "jardin," which can affect the stone's transparency. However, these inclusions give each emerald its unique personality.
- Cut: Different emerald cuts include, such as emerald cut, cushion, or oval, enhance the gem's overall beauty. The way an emerald is cut can greatly influence its color, brilliance, and overall appearance.
- Carat: The size of an emerald is often judged by weight in carats. Larger emeralds are rarer and often command higher prices.
Emerald Treatments and Synthetics
Emerald gemstones are commonly treated to enhance their appearance. Some of the common treatments include:
- Oil: This treatment involves filling surface-reaching fissures with oil to minimize their appearance and improve the stone's clarity. Oils like cedarwood oil are usually used.
- Resins: Emeralds can also be treated with resins, which have a similar refractive index to improve the stone's clarity and overall appearance.
Synthetic emeralds, also known as lab-created or man-made emeralds, have similar chemical and physical properties to their natural counterparts. However, they are created in laboratories using methods like hydrothermal growth or flux melting. Synthetic emeralds can be more affordable and have fewer inclusions than natural emeralds. Brazilian emeralds and Ethiopian emeralds are known for their exceptional color and quality; however, origins like these can sometimes command higher prices.
As you explore the world of emeralds, remember that a deeper understanding of their characteristics, origins, and treatments will help you make informed decisions when selecting the perfect gemstone for your collection or jewelry piece.
Frequently Asked Questions
How would you describe the hue of a high-quality emerald?
A high-quality emerald has a vibrant green hue that usually leans towards the slightly bluish side, often described as a rich, deep, and soothing color. The most desirable color for an emerald is a slightly bluish green tone that appears evenly saturated throughout the gemstone.
Can the color of emerald stones vary, and if so, how?
Yes, the color of emerald stones can vary due to the presence of different impurities, growth conditions, and geographical regions where they are found. Emeralds can range from very light green to dark green, with various shades and saturation levels in between. Some emeralds may even have a more yellow or bluish tone.
What is the difference between emerald green and other shades of green?
Emerald green is a specific shade of green, characterized by its slight bluish tint and rich, deep hue. This shade is distinct from other shades of green and is mainly attributed to the highly valued emerald gemstones. In contrast, other shades of green may be more yellowish, lighter, or darker, and less saturated than emerald green.
Are there emeralds that appear blue, and what are they called?
Emeralds that appear with a stronger blue hue are usually called "blue-green emeralds" or "blue emeralds." These stones have larger amounts of chromium and iron impurities, giving them a more pronounced blue appearance than the typical green emerald. Even though they're called blue emeralds, it's essential to recognize that they are still part of the emerald family.
How does the color of an emerald affect its value?
The color of an emerald significantly impacts its value. The most valued emeralds are those with a deep, rich slightly bluish-green color that is evenly distributed throughout the stone. A stone with excellent color can command high prices, even if it has visible inclusions. As the color becomes less saturated or leans more towards yellow or blue, the value of the emerald generally decreases.
What is the significance of the streak color for emeralds?
The streak color of a mineral is the color of the powdered mineral when it is rubbed on an unglazed porcelain tile called a streak plate. For emeralds, this test is not typically performed as it can damage the gemstone. Instead, the overall color and quality are assessed visually, considering the hue, saturation, and brightness, which are more crucial factors in determining an emerald's value.
Checkout some of our top collections: